Electrical Engineering Project Blogs
MPPT Based Hybrid Solar Inverter Project Using Solar and AC Charging – Complete Student Guide
🧠 Introduction
The MPPT based hybrid solar inverter project is one of the most practical and concept-rich renewable energy projects for engineering students today. It combines solar power harvesting, intelligent battery charging, and DC-to-AC inversion into a single working system that closely resembles real-world hybrid energy solutions. 🌞⚡
Unlike basic inverter projects that rely on only one power source, this project demonstrates how solar energy and AC mains can work together to ensure uninterrupted power. For students, this means deeper learning, stronger viva confidence, and a project that examiners immediately recognize as industry-relevant.
If you are aiming for strong internal marks, clear conceptual understanding, and a future-ready renewable energy project, this MPPT hybrid solar inverter is an excellent choice. 🧠✅
🎯 Project Overview and Objective
The primary objective of this project is to design and demonstrate a hybrid solar inverter system that can:
- Charge a 12 V battery using solar power through MPPT
- Automatically charge the same battery using AC mains when solar is unavailable
- Convert stored DC power into 230 V AC output to run real loads
This project is ideal for:
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering students
- Diploma and Polytechnic students
- ITI trainees and renewable energy learners
- Final-year projects, minor projects, and exhibitions
Academically, it helps students understand power conversion stages, while practically it mirrors the logic used in residential and small commercial hybrid solar systems.
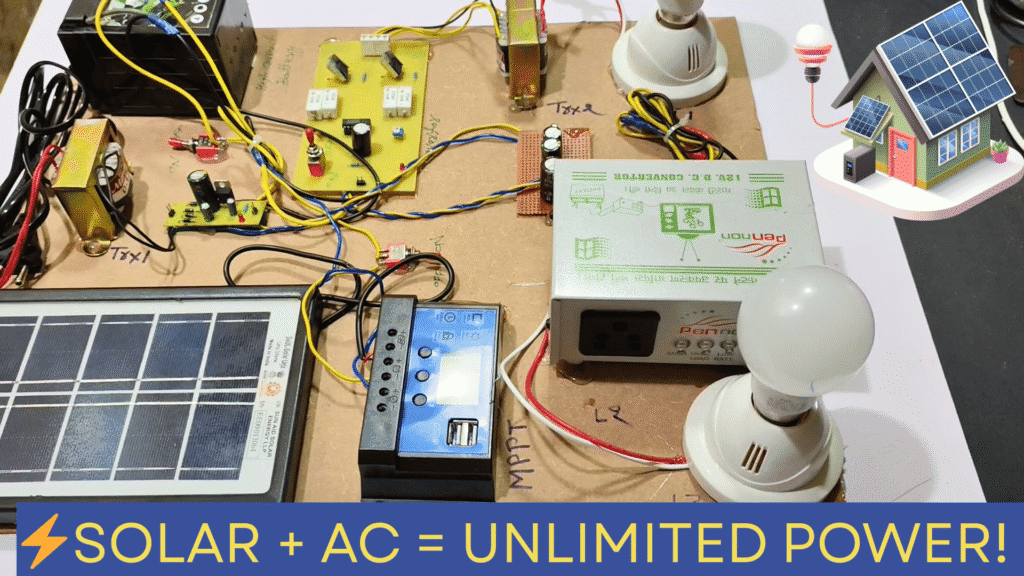
🧰 Components Used
| Component | Purpose | Why Used |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Panel | Generates DC power | Primary renewable energy source 🌞 |
| MPPT Module | Solar charge control | Extracts maximum power efficiently |
| 12 V Battery | Energy storage | Stores energy for backup operation |
| IC 4047 | Oscillator | Generates inverter switching signals |
| Power MOSFETs | Switching devices | Handle high current safely 🔌 |
| Transformer | DC to AC conversion | Steps up voltage to 230 V |
| Rectifier & Regulator | AC charging | Converts AC mains to DC |
| AC Input Section | Backup charging | Enables hybrid operation |
This component combination makes the project complete, demonstrable, and industry-aligned.
🔌 Block Diagram and Working Logic
The block diagram represents the logical flow of energy and control inside the system.

ALT: MPPT based hybrid solar inverter project block diagram explained
Block-level flow:
- Solar panel generates DC power
- MPPT module optimizes and charges the battery
- Battery supplies DC to inverter section
- Inverter converts DC to AC using IC 4047 and MOSFETs
- Transformer delivers 230 V AC output
- AC mains charging section activates when solar is absent
This structured flow makes the system easy to explain during evaluations and viva.
⚙️ Circuit Diagram and Hardware Connections
The circuit can be divided into four major sections:
- Solar Charging Section
MPPT module regulates voltage and current, ensuring safe and efficient battery charging. - AC Charging Section
A transformer, rectifier, and regulator convert 230 V AC into controlled DC for battery charging when solar input drops. - Inverter Control Section
IC 4047 generates complementary square waves required for push-pull inverter operation. - Power Stage
MOSFETs amplify current, and the transformer steps up voltage to usable AC levels.
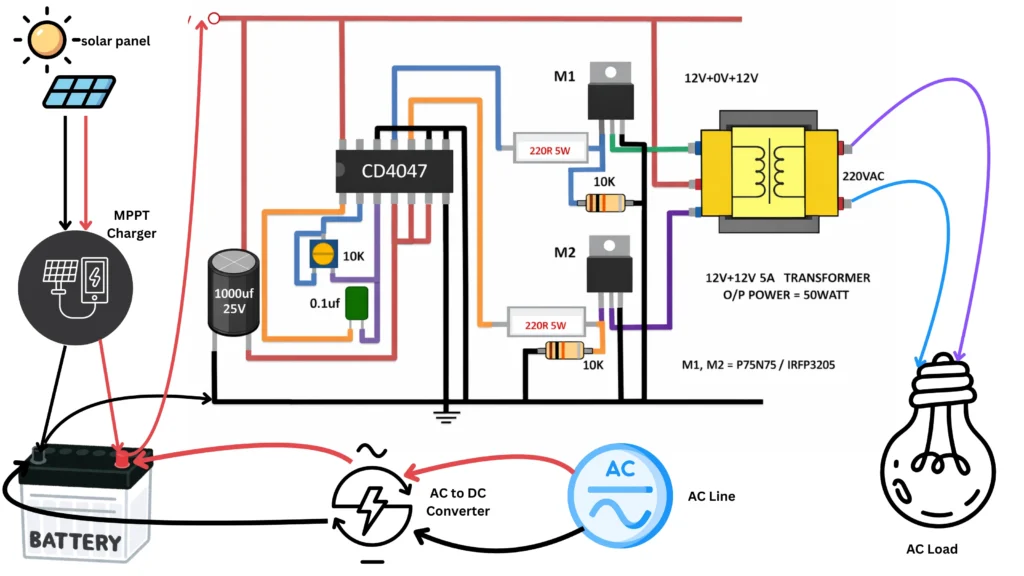
🔄 Working Principle – Step by Step
- When sunlight is available, the solar panel produces DC voltage 🌞
- The MPPT module adjusts operating point to extract maximum power
- Battery stores the optimized solar energy
- IC 4047 generates alternating control pulses
- MOSFETs switch DC through the transformer
- Transformer outputs 230 V AC for loads
- If solar input drops, AC charging automatically maintains battery level
This stepwise explanation helps students understand why each stage exists, not just what it does.
🎬 Project Demonstration 👇
Watch on YouTubeEngineering students can download the complete project documentation below. The ZIP file includes a detailed synopsis and a ready-to-use PPT for seminars, viva, and final submission.
🎓 Applications
- Academic final-year and mini projects
- Renewable energy lab demonstrations
- Solar energy training programs
- Innovation challenges and exhibitions
- Research prototypes for hybrid systems
✅ Advantages
- Strong conceptual clarity for students 🧠
- Real-world hybrid system exposure
- Ready for viva and evaluation
- Expandable for higher-level research
⚠️ Limitations
- Designed for low to medium power loads
- Not intended for heavy industrial appliances
- Educational prototype, not utility-scale system
🚀 Future Scope and Enhancements
- IoT-based battery and power monitoring 🌐
- Smart switching using microcontrollers
- AI-based energy optimization
- Wireless data logging and dashboards
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
What makes this MPPT hybrid solar inverter project suitable for final-year students?
This project covers multiple power stages including solar harvesting, intelligent charging, and inverter operation. Because it integrates theory with real hardware behavior, it scores well in evaluations and helps students confidently answer viva questions.
Can beginners understand and demonstrate this project effectively?
Yes. The project uses clear modular blocks that are easy to explain. With the provided documentation and PPT, even students new to solar systems can present it effectively. 📄✅
How does MPPT improve system efficiency compared to normal charge controllers?
MPPT continuously tracks the optimal voltage-current point of the solar panel, ensuring maximum energy extraction. This makes the system more efficient, especially during varying sunlight conditions.
Is this project expandable for advanced research or IoT integration?
Absolutely. The system can be enhanced with microcontrollers, IoT modules, and smart monitoring features, making it suitable for higher-level academic research and innovation.
Does the project include documentation for seminars and submissions?
Yes. The project includes a detailed synopsis, structured report, and presentation-ready PPT, making it fully submission-ready for colleges and universities.
🔗 Internal Resource Links
❓ FAQs
Q1. What is an MPPT based hybrid solar inverter project and why is it important for students?
A. An MPPT based hybrid solar inverter project demonstrates how solar energy and AC mains can be intelligently combined to ensure uninterrupted power supply. For students, this project is important because it covers multiple real-world concepts such as renewable energy harvesting, battery charging, inverter operation, and hybrid power management. It closely aligns with modern energy systems used in homes and industries, making it academically strong and practically relevant.
Q2. How does the MPPT technique improve the performance of the solar inverter system?
A. MPPT, or Maximum Power Point Tracking, continuously adjusts the operating point of the solar panel to extract the maximum available power under changing sunlight conditions. This significantly improves charging efficiency compared to conventional charge controllers. Understanding MPPT helps students learn advanced power electronics concepts that are commonly discussed in viva and renewable energy coursework.
Q3. Can this hybrid solar inverter project be used for final-year submissions and demonstrations?
A. Yes, this project is highly suitable for final-year and minor project submissions because it is fully functional, easy to demonstrate, and supported with proper documentation. The hybrid operation and clear block-level working make it impressive during evaluations, seminars, and exhibitions. It also allows students to confidently explain both theoretical and practical aspects.
Q4. What kind of loads can be operated using this MPPT hybrid solar inverter project?
A. The project is designed to run low to medium power AC loads such as LED bulbs, small fans, and mobile chargers. It is intended as an educational and demonstration system rather than a high-power industrial inverter. This makes it safe, classroom-friendly, and ideal for learning core inverter principles.
Q5. Is this project expandable for advanced learning or future enhancements?
A. Absolutely. The project can be enhanced by adding microcontrollers, IoT modules for monitoring battery status, or smart switching mechanisms. Such enhancements allow students to extend the project toward smart energy systems, research work, or innovation competitions without changing the core hardware concept.