Learning Resources & Tutorials
How to use Magnetic Sensor or Reed Switch
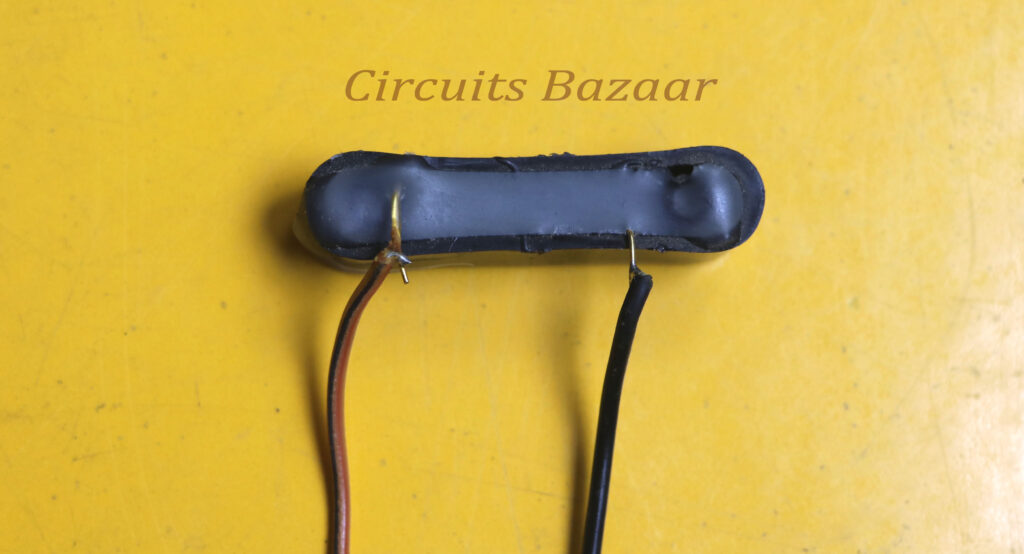
What is a magnetic reed sensor & how they work
Reed switch was invented in 1922 and later used adequately in 1936 by Walter B. Ellwood in the reed relay. A reed magnetic sensor is a sensor that uses a reed switch to detect a magnetic field. A reed switch is a switch that is activated by a magnetic field. The switch consists of a pair of ferromagnetic metal reeds that are hermetically sealed in a glass envelope. The reeds are arranged so that they are normally open (non-conducting). When a magnetic field is applied, the reeds align and the switch closes (conducting). Reed magnetic sensors are used in various applications, including security systems, door and window sensors, and automotive sensors.
Reed Sensors vs. Hall Effect Sensors?
Reed sensors and Hall effect sensors are both used to detect magnetic fields. However, there are some key differences between the two types of sensors.
Reed sensors are typically smaller than Hall effect sensors, making them more suitable for applications where space is limited. Reed sensors are also more sensitive than Hall effect sensors, meaning they can detect smaller magnetic fields. However, reed sensors are less durable than Hall effect sensors and are not suitable for applications where the sensor will be exposed to high temperatures or vibrations.
Hall effect sensors are more durable than reed sensors and can withstand exposure to high temperatures and vibrations. Hall effect sensors are also less sensitive than reed sensors, meaning they can only detect larger magnetic fields. However, Hall effect sensors are typically larger than reed sensors, making them less suitable for applications where space is limited.

Important Characteristics of Reed Sensors
Reed sensors have a number of characteristics that make them suitable for a variety of applications. Reed sensors are small and sensitive, making them ideal for applications where space is limited. Reed sensors can detect small magnetic fields, making them ideal for applications where a high degree of accuracy is required. Reed sensors are hermetically sealed, making them resistant to environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and chemicals. Reed sensors are relatively simple and inexpensive to manufacture, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
Benefits of Reed Relay
Reed relay has many benefits that make them a popular choice for a variety of applications. Reed relays are more reliable than electromechanical relays, making them suitable for applications where reliability is critical. Reed relays are smaller and lighter than electromechanical relays, making them more suitable for applications where space is limited. Reed relays have a faster switching speed than electromechanical relays, making them more suitable for applications where speed is critical. Reed relays consume less power than electromechanical relays, making them more suitable for applications where power is limited.
Two types of the reed switch
Reed switches are of two types mainly normally open and normally closed A reed switch will have three connections, two for the reeds themselves and one for the standard lead, known as the ‘arm’. The arm is connected to one of the reeds, and the other reed is connected to the common lead. When a magnetic field is applied, the reeds align and the switch closes (conducting). The strength of the magnetic field required to close the switch depends on the reed switch type.
Normally open reed switch
In a normally open reed switch, the contacts are open (non-conducting) when there is no magnetic field present. When a magnetic field is applied, the contacts close (conducting). The force required to close the contacts is known as the ‘pull-in force.
Normally closed reed switch
In a normally closed reed switch, the contacts are closed (conducting) when there is no magnetic field present. When a magnetic field is applied, the contacts open (non-conducting). The force required to open the contacts is known as the ‘break-away force.
Life of Reed Magnetic Sensor?
Reed magnetic sensors have a long life span and are typically rated for over 10 million operations. The life of reed sensors depends on the electrical load you are applying to them. Most of the time higher voltages and higher currents you apply on reed switches cause their breakdown sooner.
Advantages of Reed Relays?
Reed relays have a number of advantages over other types of relays. They are smaller and more sensitive than other types of relays, making them ideal for use in applications where space is limited. Reed relays can also switch faster than other types of relays, making them ideal for use in high-speed applications. Hall effects are certainly appropriate for some types of applications, but reed switches have superior electrical isolation to their solid-state counterparts in most applications, and they face less electrical resistance due to closed contacts. Reed relays are also more resistant to shock and vibration than other types of relays, making them ideal for use in harsh environments.
Complications in using reed sensors?
Reed switches are generally reliable, but they can be susceptible to false triggering if they are exposed to electromagnetic fields or static electricity. They can also be damaged by excessive voltage or current.
What size magnet do I need to activate the reed sensor?
The size of the magnet needed to activate a reed sensor depends on the sensor itself. Generally, a stronger magnet is needed to activate a sensor from a further away distance.


Application:
- Can be used in extreme temperatures or other harsh environmental conditions.
- HDD read-heads / Fluxgates / Transmission coils
- ABS ( Anti Lock Braking System )sensors
- open and closing of automatic doors.
- Can Be Used in moist or humid environments where normal sensors don’t work such as dishwashers, refrigerators
- Can be used in Automation and manufacturing. Reed sensors have countless practical applications in Manufacturing Plants Like Conveyor belts, cylinder pistons, and automated factory machinery all use reed sensors to detect limits and facilitate on/off functionality of particular operations in the machines.
- Can be Used in Automotive Industry to meet strict standards that protect against failure
- Can be used in security systems to know the status of doors/windows whether they are open or closed.
- Can be used in medical instruments such as pacemakers use reed sensors to provide efficient, reliable circuitry operations with minimal maintenance requirements
- Can be Used in Gym Equipments, as reed sensors act as speed sensors in bicycle wheels and treadmills in the gym.

