Electronics Engineering Project Blogs
Driver Drowsiness Detection Project Using Raspberry Pi Pico – Complete Engineering Guide
🧠 Introduction
A driver drowsiness detection project is no longer just an academic experiment. With increasing road accidents caused by fatigue and alcohol consumption, such systems have become a real necessity in modern vehicle safety design.
In this project, we build a real-time driver safety system that continuously monitors eye blink patterns to detect drowsiness and checks alcohol presence before allowing vehicle operation. When unsafe conditions are detected, the system automatically disables the vehicle engine and alerts the driver.
For engineering students, this project is powerful because it combines embedded systems, sensors, safety logic, and real-world relevance—all of which directly improve understanding, confidence, and evaluation performance.
Project Overview & Objective
The objective of this project is to design a vehicle safety system that actively prevents accidents instead of only warning the driver.
Key goals:
- Detect driver drowsiness using an eye blink sensor
- Detect alcohol consumption using an alcohol sensor
- Automatically turn OFF the vehicle engine using a relay
- Provide audio alerts and visual feedback
- Display system status on a 16×2 LCD
This project is ideal for Diploma and B.Tech students working on embedded systems, safety automation, or vehicle-related final-year projects.
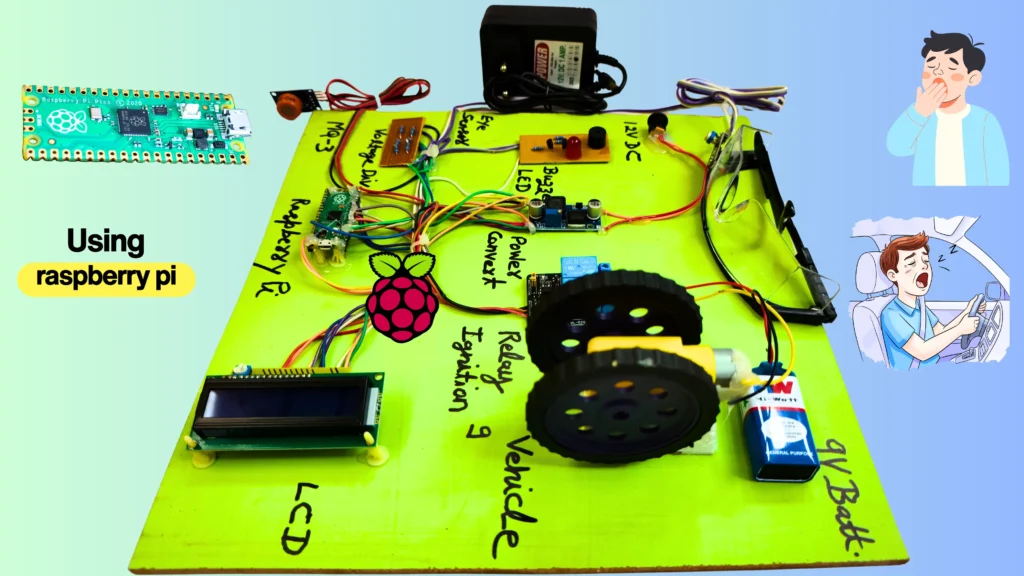
Components Used
| Component | Purpose | Why Used |
|---|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi Pico | Main controller | Fast, reliable, 3.3V logic MCU |
| IR Eye Blink Sensor | Drowsiness detection | Simple, effective, real-time |
| Alcohol Sensor | Alcohol detection | Prevents unsafe driving |
| Relay Module | Engine control | Electrical isolation and safety |
| Buzzer + LED | Alert system | Immediate driver warning |
| 16×2 LCD | Status display | Clear real-time feedback |
| LM2596 Buck Converter | Power regulation | Stable 5V supply |
| Voltage Divider | Signal protection | Converts 5V to 3.3V safely |
Block Diagram & Working Logic
The block diagram represents the flow of signals and decisions inside the system.
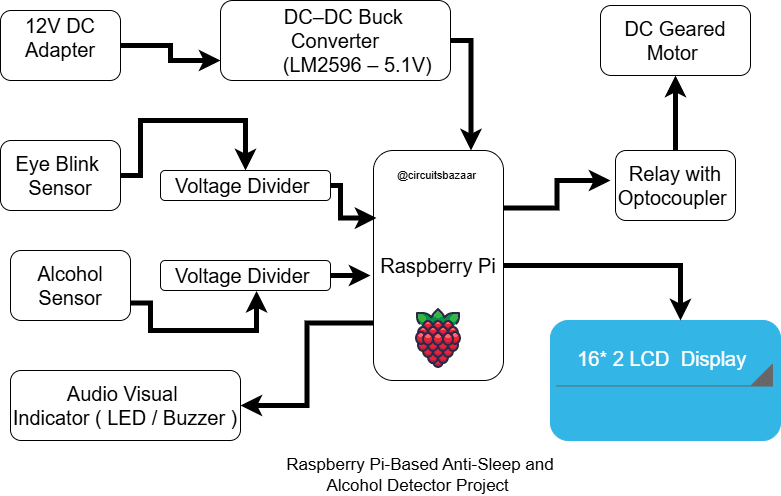
Logic Flow:
- Sensors continuously monitor driver condition
- Sensor outputs are safely level-shifted to 3.3V
- Raspberry Pi Pico processes the inputs
- Relay and buzzer are controlled based on safety logic
- LCD displays system status in real time
Alcohol detection is given higher priority than drowsiness detection.
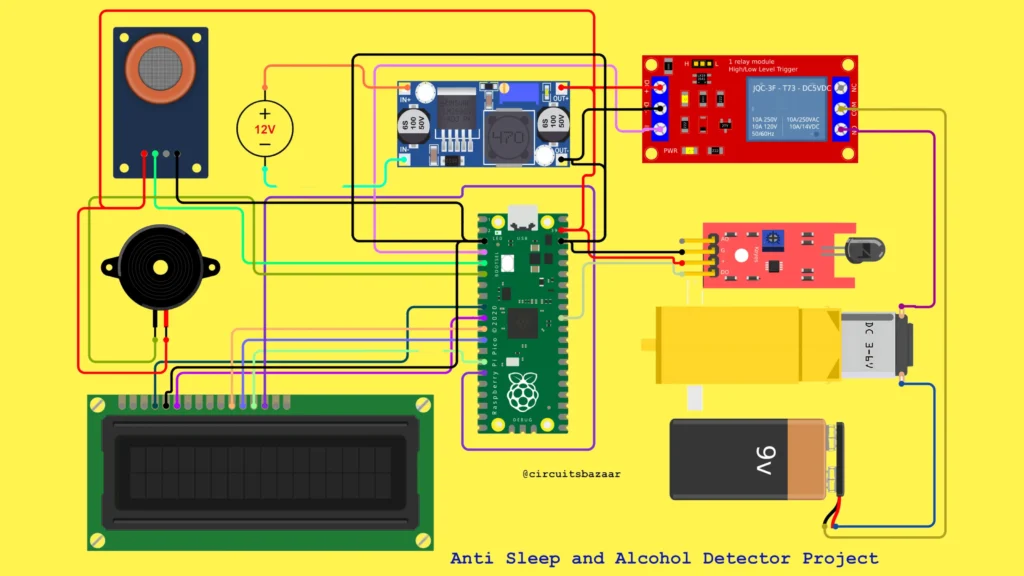
Circuit Diagram & Hardware Connections
Hardware Sections:
- Power Supply:
12V adapter → LM2596 buck converter → 5.1V → Pico VSYS - Sensor Interface:
IR and alcohol sensor outputs pass through voltage dividers - Output Section:
Relay controls motor, buzzer provides alerts, LCD shows messages
The motor is powered using a separate supply, ensuring electrical isolation.
Working Principle (Step-by-Step)
- System powers ON and initializes
- LCD shows system ready message
- Alcohol sensor is checked first
- If alcohol is detected, engine is immediately turned OFF
- If no alcohol is detected, eye blink sensor is monitored
- Prolonged eye closure triggers drowsiness detection
- Relay turns OFF the engine and buzzer alerts the driver
- If both conditions are safe, the vehicle operates normally
This logic ensures fail-safe operation.
Embedded Code (Arduino IDE – Raspberry Pi Pico)
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
LiquidCrystal lcd(6,7,8,9,10,11);
#define IR_SENSOR 26
#define RELAY_PIN 2
#define ALCOHOL_SENSOR 3
#define BUZZER_PIN 4
void setup() {
pinMode(IR_SENSOR, INPUT);
pinMode(ALCOHOL_SENSOR, INPUT);
pinMode(RELAY_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BUZZER_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(BUZZER_PIN, HIGH);
lcd.begin(16,2);
lcd.print("System Ready");
}
void loop() {
if(digitalRead(ALCOHOL_SENSOR) == LOW) {
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(BUZZER_PIN, LOW);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("Alcohol Detected");
delay(100);
}
else if(digitalRead(IR_SENSOR) == HIGH) {
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(BUZZER_PIN, LOW);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("Drowsy Detected");
delay(100);
}
else {
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(BUZZER_PIN, HIGH);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("Driver OK");
delay(200);
}
}Code Explanation
The code continuously checks alcohol detection first, then eye blink status. Relay and buzzer outputs are controlled using active-low logic to ensure safe engine cutoff.
- The program starts by initializing the Raspberry Pi Pico GPIO pins for the eye blink sensor, alcohol sensor, relay, and buzzer, ensuring that sensors are read as inputs and actuators are controlled as outputs.
- During system startup, the relay is kept ON (engine allowed) and the buzzer is turned OFF, which ensures a safe default state where the vehicle can operate normally unless an unsafe condition is detected.
- The code continuously checks the alcohol sensor first, giving it the highest priority. If alcohol is detected, the relay is immediately turned OFF to stop the vehicle, and the buzzer is activated to alert the driver.
- If no alcohol is detected, the system then monitors the eye blink sensor. A prolonged eye closure is treated as driver drowsiness, and the relay is again turned OFF while the buzzer remains ON to warn the driver.
- When neither alcohol nor drowsiness is detected, the system allows normal vehicle operation by keeping the relay ON and buzzer OFF, and the LCD displays a safe driving message.
- Throughout operation, the 16×2 LCD provides real-time feedback, helping the driver and evaluator understand whether the system is in normal mode or safety cutoff mode.
🎥 Project Demonstration Video
Hindi Demonstration 👇
English Demonstration 👇
Engineering students can download the complete project documentation below. The ZIP file includes a detailed synopsis and a ready-to-use PPT for seminars, viva, and final submission.
🛒 Want a Fully Assembled Version of This Project?
If you are a student who wants to focus on understanding, demonstration, and viva instead of hardware troubleshooting, you can directly use the fully assembled driver drowsiness detection project available on Circuits Bazaar.
Applications
- Academic final-year projects
- Vehicle safety research models
- Driver monitoring systems
- Embedded system demonstrations
- Innovation and competition projects
Advantages
- Real-time safety enforcement
- Strong viva and evaluation impact
- Practical embedded learning
- Ready-to-use architecture
Limitations
- Sensor calibration required
- Environmental sensitivity
- Prototype-level vehicle simulation
Future Scope & Enhancements
- GPS and GSM alert integration
- Mobile application monitoring
- AI-based eye tracking
- Cloud-based data logging
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
What makes this driver drowsiness detection project suitable for final-year students?
This project combines real-world relevance with practical embedded system design. Students can clearly explain sensor logic, safety decisions, and hardware integration during viva and evaluations.
Is this project based on real-time detection or simulation?
It is a real-time working system using physical sensors and relay-based engine control. No simulation or software-only logic is used.
Can beginners understand this project?
Yes. The logic flow is simple, and the system behavior is clearly visible through the LCD, buzzer, and motor control.
Does this project include documentation for submission?
Yes. A detailed synopsis, PPT, and report are provided to support seminars, viva, and final submission.
Can this project be expanded further?
Yes. It can be enhanced with IoT, AI-based eye tracking, wireless communication, and cloud monitoring features.